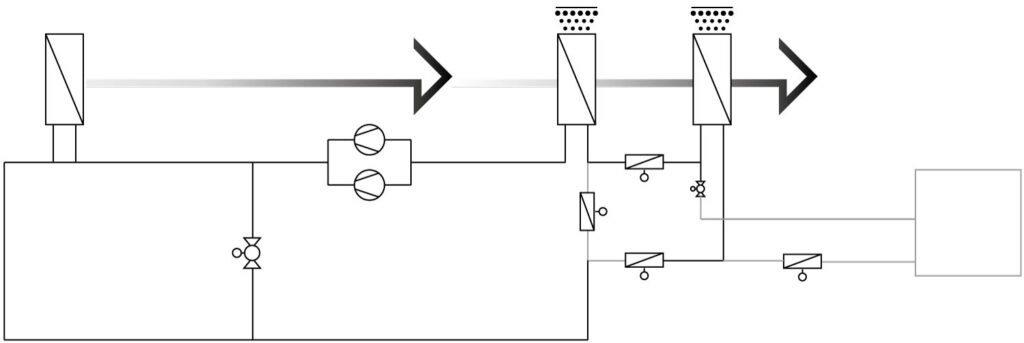
CHILLER HEAT REJECTION USING AN ENERGY RECOVERY SYSTEM
The ERS heat exchanger in the exhaust air is divided into sections. The first part is always used as an ERS heat exchanger. The second part is used as an ERS heat exchanger in winter and as heat rejection for the chiller in summer.
EFFICIENT SOLUTION FOR COOLING THE OUTSIDE AIR
Chiller heat rejection can be done efficiently and economically using a multi-functional ERS. This approach allows external cooling towers to be downsized or often eliminated entirely.
This eliminates or reduces:
- Insulation of sound emissions from cooling towers
- Structural measures for external cooling towers
- Building infrastructure for external cooling towers
- Unpleasant building aesthetics
USE IN SUMMER
In summer, the first heat exchanger in the exhaust air is used to cool the water/glycol circuit, while the second heat exchanger is provided for heat rejection for the chiller. To achieve the highest possible efficiency of the chiller and the overall system, the heat rejection heat exchanger is equipped with a sprinkler system. By directly wetting the large fin surfaces, the temperature is significantly reduced.
By pre-cooling the water/glycol mixture in the exhaust air, the chiller can be smaller.
USE IN WINTER
In winter, when no cooling is required, both heat exchangers are connected in series in the exhaust air and used to recover heat. By doing this, the total capacity of both heat exchangers can be used in different combinations depending on demand.
Summer operation
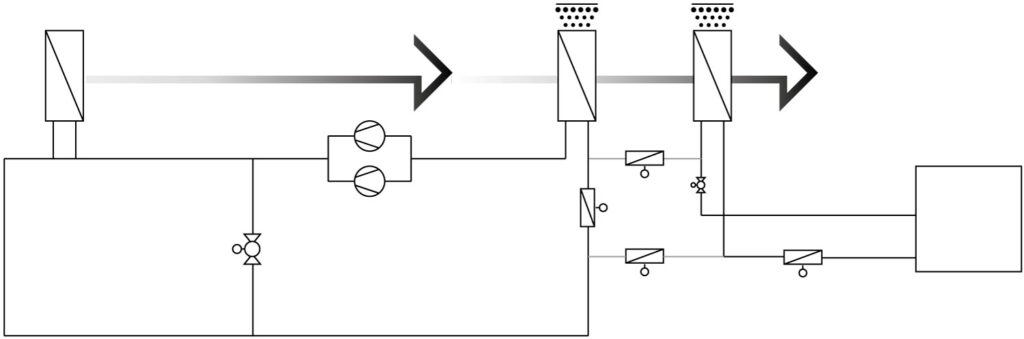
Winter operation